|
|
||||
|
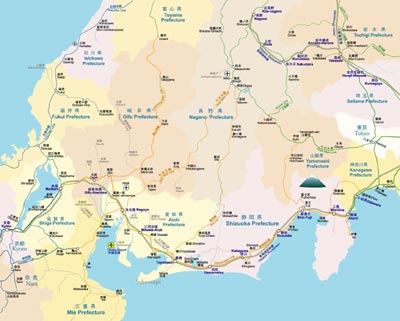
The Tōkai region (東海地方 Tōkai-chihō) is a sub-region of the Chūbu region in Japan that runs along the Pacific Ocean. The name means "East sea" and comes from the Tōkaidō, one of the Edo Five Routes. Because Tōkai is a sub-region and is not officially classified, there is some disagreement about where exactly the region begins and ends, however Japanese maps widely conclude that the region includes Shizuoka, Aichi, Gifu and Mie prefectures. The largest major city in the region is Nagoya and the Chūkyō Metropolitan Area (Nagoya Metropolitan Area) makes up a large portion of the region and has Japan's third strongest economy. The business influence of this urban area sometimes extends out into the outlying areas of the three prefectures centered around Nagoya which are Aichi, Gifu, and Mie; this area is sometimes referred to as the Chūkyō region. Tōkai is a heavy manufacturing area and is one of the most industrial regions in Japan. Its coast is lined with densely populated cities with economies that thrive on factories. The Tōkai region has experienced a number of large earthquakes in the past, including the two great earthquakes in 1944 (also known as the "Tonankai earthquake") and 1945 (also known as the "Mikawa earthquake"). Following the work of Kiyoo Mogi, it is predicted that there is a possibility that the area will be subject to a shallow magnitude 8.0 earthquake in the near future. Nagoya, Shizuoka, and other large cities would be greatly damaged, with casualties in the thousands, if not millions, making it one of the worst disasters on Earth. The Coordinating Committee for Earthquake Prediction designated the region as an Area of Specific Observation in 1970, and upgraded it to an Area of Intensified Observation in 1974.
|
||||